We all know that sugar can tantalize our taste buds, but what about the sweeteners that tantalize your taste buds while also keeping a sugar intake under control? Allulose and Stevia stand out as promising alternatives. Are they really the same or do they dance to different sugary songs?
Simply put, Allulose and Stevia sweeten your favorite treats, but their paths differ in terms of origin, taste, and health benefits. As we go over their molecular structures and investigate the sweetness levels, you will realize that the characteristics that set them apart are what distinguish them from the competition.
Learn how to pronounce Stevia and how to pronounce Allulose while we travel to the regions where they are used. With this article, you will learn about the latest scientific findings as well as the mysteries behind their flavors, allowing you to make informed decisions about your sweet indulgences. It’s time to go all out for the delectable world of stevia and allulose.
Allulose: Nature, Origin, and Composition
Nestled within the realm of alternative sweeteners, Allulose emerges as a distinctive player, captivating taste buds while addressing the growing concern of sugar intake. Defined as a rare sugar, Allulose is naturally found in small quantities in certain fruits and grains, with notable sources including figs, raisins, and wheat. This rarity adds an element of exclusivity to Allulose, making it an intriguing choice for those seeking sweetness without the caloric burden.
The extraction process of Allulose unveils a meticulous journey from its natural sources to the crystalline form we encounter in various products. Through advanced techniques, this sweetener is extracted from natural sources, undergoing a series of purification steps to achieve the desired purity. This process ensures that the final product retains its sweetening prowess while embodying the essence of its natural origins.
Delving into the chemical composition and molecular structure of Allulose reveals the secrets behind its unique characteristics. Comprising the same atoms as traditional sugars but arranged differently, Allulose’s molecular structure contributes to its sweetness without the associated calories. This distinctive arrangement confounds our taste receptors, providing a sweet experience without the metabolic consequences linked to traditional sugars.
Unveiling Allulose’s Secrets: A Closer Look
Definition and Natural Sources: Allulose, often referred to as “nature’s sweet secret,” is characterized by its low-calorie content and natural occurrence in select fruits. This rarity grants Allulose a certain allure, prompting a surge in its popularity among health-conscious consumers seeking guilt-free sweetness. As a monosaccharide, Allulose stands out for its unique sweetness profile, offering an alternative that mimics the taste of sugar without the caloric baggage.
Extraction Process: The journey from orchards to your favorite treats involves a meticulous extraction process. Initially sourced from fruits like jackfruit and kiwi, Allulose undergoes purification steps to isolate and concentrate its sweetness. This refined extraction process ensures the final product retains its natural charm while meeting the standards of purity demanded by the culinary world. The result is a versatile sweetener that seamlessly integrates into various recipes, offering a palatable option for those mindful of their sugar intake.
Chemical Composition and Molecular Structure: Beyond its delectable taste, the allure of Allulose lies in its molecular dance. Composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms like traditional sugars, Allulose distinguishes itself through its unique arrangement. This molecular structure, a mirror image of fructose, confounds our taste buds. While it triggers the sweet receptors on our tongues, it does so without the caloric aftermath associated with its more commonplace counterparts. This chemical magic grants Allulose the status of a low-calorie sweetener, contributing to its rising prominence in the culinary landscape.
In the intricate world of sweeteners, Allulose stands as a testament to the marriage of nature and science. From its humble beginnings in fruits to the advanced extraction processes that bring it to our tables, this sweet secret continues to redefine our approach to sweetness, offering a tantalizing experience without the usual caloric trade-offs. As consumers increasingly prioritize healthier alternatives, Allulose emerges as a frontrunner, sweetening the deal for those seeking a guilt-free indulgence.
Stevia: A Natural Sweetener with a Plant Origin
In the vibrant spectrum of natural sweeteners, Stevia emerges as a botanical marvel, captivating palates with its distinct sweetness derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant. As we embark on an exploration of this green-hued sweetness, we unravel the layers of Stevia’s origin, the intricate art of extraction, and the profound impact of its chemical composition on our taste experience.
Introduction to Stevia and Its Natural Sources: Stevia, often hailed as nature’s sweet secret, finds its roots in the sprawling landscapes where the Stevia rebaudiana plant thrives. Native to South America, this perennial shrub’s leaves conceal a sweetness that surpasses that of traditional sugar. The introduction of Stevia to the global culinary stage has been transformative, offering a natural alternative to sweeten our favorite dishes and beverages. Its popularity stems not only from its sweetening prowess but also from being a zero-calorie, plant-derived substitute, aligning seamlessly with the demands of health-conscious consumers.
Extraction Methods and the Role of Glycosides: The journey from Stevia leaf to sweetener involves delicate extraction methods that preserve its inherent qualities. The leaves, rich in sweet compounds known as glycosides, undergo a meticulous process to extract the sweetness without compromising the plant’s natural essence. Among these glycosides, stevioside and rebaudioside A stand out as primary contributors to Stevia’s sweetness. Through various extraction techniques, including water extraction and ethanol precipitation, these glycosides are concentrated to form the potent Stevia sweeteners we find on shelves. The role of glycosides in Stevia not only defines its sweetness but also contributes to its clean, refreshing taste, setting it apart from other sugar substitutes.
Decoding Stevia’s Essence: A Closer Look
Chemical Composition and Structure: Central to Stevia’s allure is its unique chemical composition. Comprising diterpene glycosides, these compounds bestow the sweet taste associated with Stevia leaves. The steviol glycosides within Stevia have garnered attention for being up to 300 times sweeter than sucrose, the standard table sugar. The magic lies in their molecular structure, where the glycosides, anchored to a steviol backbone, deliver sweetness without the caloric load. This structural uniqueness not only defines Stevia’s appeal but also positions it as a formidable contender in the realm of natural sweeteners.
As we traverse the landscape of Stevia’s natural origins, extraction methods, and chemical intricacies, a picture emerges of a sweetener deeply rooted in nature yet intricately crafted to satisfy modern taste preferences. Stevia, with its plant-derived sweetness and zero-calorie attributes, is not just a sweetener; it’s a testament to the harmonious fusion of science and nature, offering a flavorful alternative that transcends the limitations of traditional sugar. So, whether it’s a steaming cup of tea or a decadent dessert, Stevia invites us to savor the sweetness of the natural world, one leaf at a time.
Flavor Profile and Taste Characteristics
In the realm of alternative sweeteners, the journey of taste becomes a paramount consideration, steering us through the nuanced landscapes of Allulose and Stevia. These two sweet titans, each armed with its distinct flavor profile, redefine our sensory experience, making the choice between them a matter of personal preference and culinary finesse.
Allulose: Describing the Taste and Mouthfeel: Allulose, often hailed as the “virtuous sugar,” introduces our palates to a taste remarkably reminiscent of traditional sucrose. Its sweetness dances on the taste buds with a similar intensity, delivering a satisfying sweetness without the caloric baggage. The flavor journey takes an intriguing turn as Allulose, despite its sugar-like sweetness, concludes with a cooling sensation – a unique characteristic setting it apart from its conventional counterpart. This cooling effect adds a layer of sophistication to its taste profile, making it an enticing option for those seeking a sugar substitute that feels as good as it tastes.
Mouthfeel: The mouthfeel of Allulose further enhances its allure. Unlike some artificial sweeteners notorious for leaving an unpleasant aftertaste, Allulose offers a clean and smooth finish. This velvety texture seamlessly integrates into a myriad of culinary creations, from beverages to baked goods, preserving the indulgent feel of traditional sugar without the caloric ramifications.
Stevia: Exploring Its Unique Flavor Profile: On the other side of the sweet spectrum, Stevia unfolds its unique flavor profile derived from the glycosides within its leaves. Stevia’s sweetness, while potent, carries a nuanced herbal undertone, introducing a layer of complexity to its taste. The initial sweetness, akin to the bright notes of traditional sugar, is accompanied by subtle herbal nuances that distinguish Stevia as a plant-derived sweetener. As with any natural element, the taste of Stevia varies between individuals, with some detecting a mild licorice-like flavor, adding to the intrigue of this botanical sweetener.
Mouthfeel: Stevia’s mouthfeel possesses a clean and refreshing quality. Unlike the lingering sensations associated with some sugar substitutes, Stevia’s aftertaste is minimal, allowing the natural flavors of dishes to shine through. This clean finish positions Stevia as a versatile sweetener, capable of elevating the taste of everything from beverages to desserts.
A Comparative Analysis of the Taste Differences: When we embark on a comparative analysis of the taste differences between Allulose and Stevia, a distinctive narrative unfolds. Allulose, with its sugar-like sweetness and cooling finish, caters to those yearning for a close alternative to traditional sugar. Stevia, with its herbal notes and clean finish, appeals to those who prefer a more botanical sweetness.
Deciphering the Sweet Symphony: A Closer Look
Comparative Notes:
- Intensity of Sweetness: Allulose mirrors the sweetness of sugar, while Stevia offers a potent sweetness with herbal nuances.
- Aftertaste: Allulose boasts a clean and smooth finish, whereas Stevia’s aftertaste is minimal, allowing the natural flavors to prevail.
- Versatility: Both sweeteners seamlessly integrate into various recipes, providing flexibility in culinary applications.
In the intricate world of flavor profiles and taste characteristics, the choice between Allulose and Stevia becomes a nuanced dance of preferences. Whether it’s the familiar sweetness of Allulose or the herbal charm of Stevia, these alternatives invite us to savor sweetness in a myriad of ways, adding a touch of culinary sophistication to our diverse palates.
Sweetness Levels and Usage in Culinary Applications
In the culinary realm, sweetness is not just a taste but a symphony that defines the success of a dish. As we delve into the sweet dynamics of Allulose and Stevia, we embark on a journey exploring their sweetness intensity, applications in cooking and baking, and a nuanced breakdown of their compatibility in diverse recipes.
Allulose’s Sweetness Intensity Compared to Traditional Sugar: Allulose, hailed for its virtue as a low-calorie sweetener, mirrors the sweetness of traditional sugar, offering a comparable taste experience without the caloric baggage. However, the intensity of Allulose’s sweetness is slightly lower than sucrose, providing a refined sweetness that doesn’t overwhelm the palate. This nuanced balance makes Allulose an ideal choice for those seeking a sugar substitute that aligns with their health-conscious lifestyle without compromising on the delightful sweetness integral to culinary endeavors.
Stevia’s Sweetness Level and Applications in Cooking and Baking: Stevia, derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, presents a sweetness level that surpasses traditional sugar with its glycosides, namely stevioside and rebaudioside A. Approximately 200 to 300 times sweeter than sucrose, Stevia introduces a potent sweetness that necessitates careful measurement in culinary applications. In cooking and baking, Stevia’s versatility shines as it can withstand high temperatures without losing its sweetening prowess. Its heat-stable nature opens the door to a myriad of applications, from sweetening beverages to contributing to the delightful texture of baked goods.
A Breakdown of Compatibility in Different Recipes: Allulose:
- Beverages: Allulose seamlessly integrates into beverages, providing a sweet undertone without compromising the drink’s overall flavor.
- Baking: Ideal for baking, Allulose contributes to the desired texture and sweetness, making it a versatile choice for cakes, cookies, and pastries.
- Sauces and Dressings: Allulose dissolves easily, making it a perfect addition to sauces and dressings, ensuring a harmonious blend of flavors.
Stevia:
- Beverages: Stevia’s potent sweetness makes it a suitable candidate for beverages, requiring minimal quantities to achieve the desired sweetness level.
- Baking: In baking, Stevia excels in recipes where its unique herbal undertones complement the overall flavor profile. It may require experimentation to find the right balance.
- Desserts: Stevia shines in desserts where its sweetness enhances the natural sweetness of fruits, creating a delightful and guilt-free indulgence.
A Harmonious Duo: Both Allulose and Stevia exhibit versatility in culinary applications, but their harmonious pairing can elevate the sweetness experience. Combining these sweeteners allows for a synergistic approach, balancing the refined sweetness of Allulose with the potent intensity of Stevia. This combination provides a comprehensive sweetness profile that caters to a diverse range of recipes, ensuring that health-conscious individuals can savor the joys of sweetness without compromising on taste.
Decoding the Sweet Symphony: A Closer Look
In the intricate dance of sweetness levels and culinary applications, Allulose and Stevia emerge as virtuosos, each bringing its unique strengths to the table. Whether it’s the refined sweetness of Allulose or the potent intensity of Stevia, these sweet alternatives invite us to embark on a flavorful journey where health-conscious choices seamlessly intertwine with the joy of indulgence.
Impact on Blood Sugar and Insulin Levels
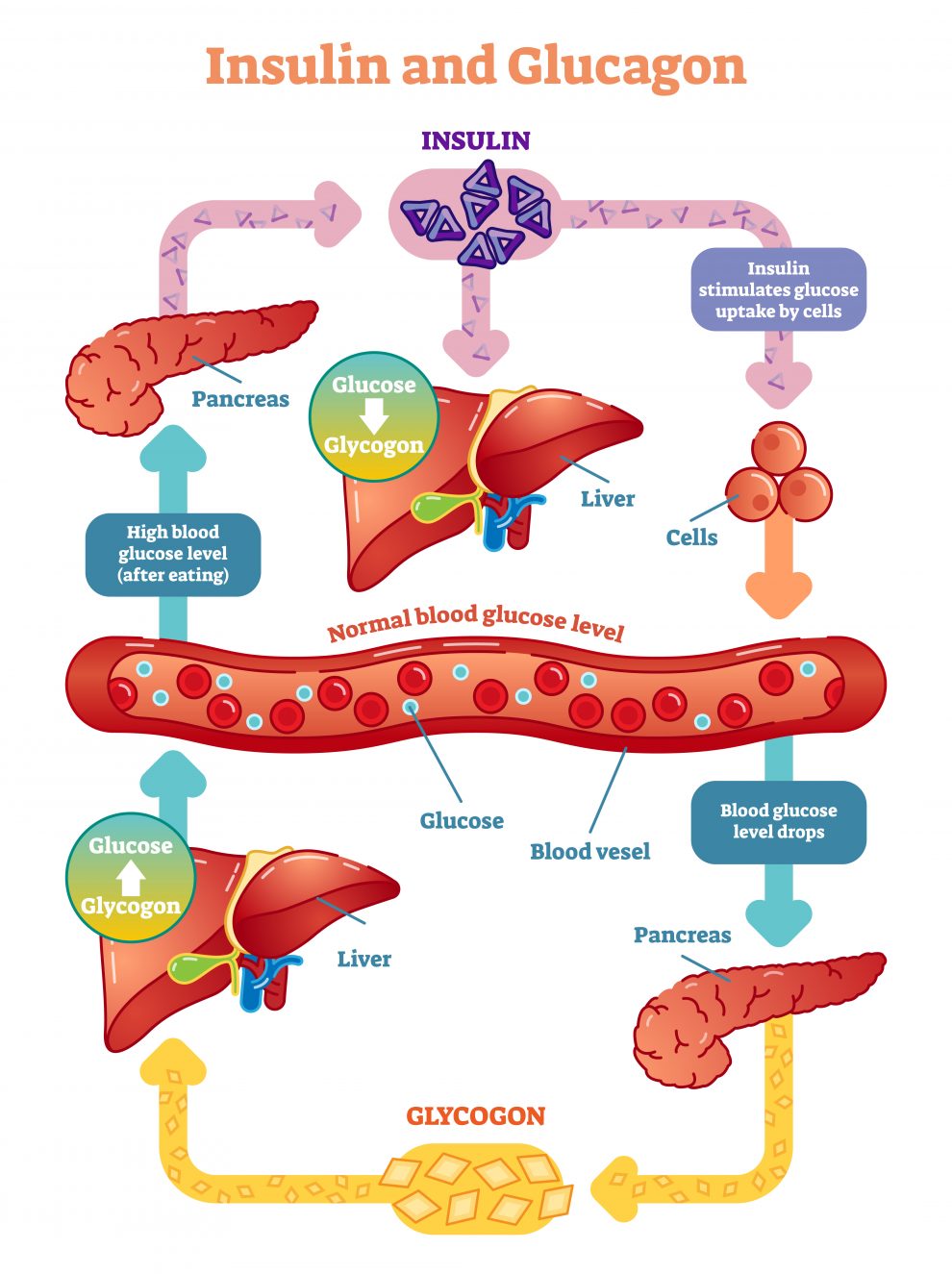
In the pursuit of healthier alternatives to traditional sugar, understanding the impact on blood sugar and insulin levels becomes paramount. Allulose and Stevia, both celebrated for their low-calorie attributes, navigate the metabolic landscape in distinct ways, prompting a closer examination of their influence on glycemic index and insulin response.
Allulose: Examining Its Glycemic Index and Effect on Blood Sugar: Allulose, a rare sugar found in nature, has gained attention for its minimal impact on blood sugar levels. With a negligible glycemic index, Allulose is absorbed into the bloodstream but undergoes limited metabolism, resulting in little to no increase in blood glucose. This unique characteristic positions Allulose as a valuable sweetener for individuals mindful of their blood sugar levels. The steady rise in popularity of Allulose stems not only from its ability to sweeten without spiking blood sugar but also from its potential to be included in the diets of those managing conditions like diabetes.
Analyzing Its Impact on Insulin Response: The influence of Allulose on insulin response is equally noteworthy. Studies suggest that Allulose does not significantly stimulate insulin secretion, making it an attractive option for those seeking sweet alternatives without the insulin fluctuations associated with traditional sugars. This characteristic renders Allulose a potential ally for individuals aiming to maintain stable insulin levels, an essential consideration in the context of metabolic health.
Stevia: Analyzing Its Impact on Insulin Response: Stevia, sourced from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, imparts sweetness without contributing calories, a feature that positions it favorably in the world of sugar substitutes. While Stevia does not raise blood sugar levels, its impact on insulin response is a subject of interest. Studies suggest that Stevia may even have a potential role in improving insulin sensitivity, making it an intriguing option for those with insulin-related concerns. However, it’s crucial to note that individual responses may vary, and further research is ongoing to unravel the intricacies of Stevia’s interaction with insulin.
A Comparative Study on the Metabolic Effects of Both Sweeteners: Allulose:
- Glycemic Index: Negligible, making it a suitable choice for those monitoring blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Response: Limited impact on insulin secretion, potentially beneficial for maintaining stable insulin levels.
Stevia:
- Glycemic Index: Negligible, aligning with a low impact on blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Response: Studies suggest potential benefits for insulin sensitivity, contributing to metabolic health.
A Deeper Dive into Metabolic Harmony: A Closer Look
As we navigate the metabolic effects of Allulose and Stevia, a nuanced understanding emerges. Allulose, with its minimal impact on blood sugar and limited stimulation of insulin secretion, caters to the needs of those aiming for metabolic stability. Stevia, on the other hand, not only shares these attributes but also hints at potential benefits for insulin sensitivity. The choice between these sweeteners becomes not only a matter of taste but a strategic decision aligning with individual health goals. In the dynamic landscape of metabolic health, Allulose and Stevia present themselves as allies, offering a sweet symphony without compromising the delicate balance of blood sugar and insulin levels.
Health Benefits and Concerns
In the quest for sweet alternatives that align with health-conscious lifestyles, Allulose and Stevia emerge as contenders, each bearing a unique set of potential health benefits and associated concerns. Navigating the nuanced landscape of these sweeteners requires a closer look at their individual attributes, shedding light on their positive contributions and considerations for mindful consumption.
Allulose: Potential Health Benefits and Associated Concerns: Potential Health Benefits:
- Low-Calorie Option: Allulose, with its low-calorie profile, stands out as an attractive alternative for those seeking sweetness without the caloric load of traditional sugar.
- Blood Sugar Impact: Studies suggest that Allulose may have minimal impact on blood sugar levels, positioning it favorably for individuals managing conditions like diabetes.
Associated Concerns:
- Gastrointestinal Effects: Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort, including bloating or laxative effects, when consuming Allulose in excessive amounts.
- Limited Research: While initial studies are promising, the long-term effects of Allulose consumption warrant further research to fully understand its implications on metabolic health.
Stevia: Examining Its Positive Health Attributes and Potential Drawbacks: Positive Health Attributes:
- Zero Calories: Stevia, a zero-calorie sweetener, addresses the concerns associated with excess caloric intake, supporting weight management goals.
- Potential Insulin Sensitivity: Research hints at Stevia’s potential role in improving insulin sensitivity, making it a potentially favorable option for those with insulin-related concerns.
Potential Drawbacks:
- Aftertaste: Some individuals may perceive a mild aftertaste with Stevia, which could impact the overall taste experience.
- Processing Methods: Concerns may arise regarding the processing methods used to extract Stevia sweeteners, prompting scrutiny over the purity of the final product.
An Objective Evaluation of the Overall Health Implications: Balanced Consumption Guidelines:
Allulose: Moderation is key when incorporating Allulose into one’s diet to mitigate potential gastrointestinal effects. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance.
Stevia: Given its zero-calorie nature, Stevia offers a health-conscious alternative, but individual preferences for taste may influence its adoption.
Overall Health Implications: While both Allulose and Stevia present themselves as viable alternatives to traditional sugar, their health implications underscore the importance of moderation and individual considerations. Allulose’s potential benefits in blood sugar management and Stevia’s role in weight control and insulin sensitivity position them as allies in the pursuit of healthier dietary choices. The key lies in informed and mindful consumption, recognizing that while these sweeteners offer advantages, a balanced approach to sweetness contributes to holistic well-being.
Deciphering the Sweet Code: A Closer Look
In the intricate tapestry of health benefits and concerns, Allulose and Stevia emerge as dynamic players, offering a bridge between sweet indulgence and mindful wellness. As individuals navigate the choices in the realm of sweeteners, understanding the nuances of these sugar substitutes allows for informed decisions that harmonize with individual health goals. In the grand symphony of health-conscious living, Allulose and Stevia contribute their unique notes, inviting us to savor sweetness with a dash of prudence.
Regulatory Approvals and Safety

In the landscape of alternative sweeteners, the journey towards widespread acceptance is paved with regulatory validations and meticulous safety assessments. Both Allulose and Stevia, as contenders in the realm of sugar substitutes, undergo scrutiny to ensure their compliance with regulatory standards and to address safety considerations.
Allulose: Regulatory Status and Safety Considerations: Regulatory Status:
- Allulose has achieved regulatory approval in various countries, including the United States, where it received Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- The European Union also recognizes Allulose as a novel food.
Safety Considerations:
- Numerous studies support the safety of Allulose consumption, emphasizing its low caloric impact and minimal effect on blood sugar levels.
- Some individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal effects at higher doses, underscoring the importance of moderation in consumption.
Stevia: Overview of Regulatory Approvals and Safety Assessments: Regulatory Approvals:
- Stevia, sourced from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, has gained regulatory approval globally, including recognition by the FDA as GRAS.
- The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated and approved certain Stevia glycosides for use in the EU.
Safety Assessments:
- Extensive safety assessments affirm the benign nature of Stevia, particularly in relation to blood sugar levels and caloric intake.
- While generally considered safe, some individuals may perceive a mild aftertaste, and the processing methods for Stevia extract can be a subject of consideration.
A Comparative Analysis of the Safety Profiles of Both Sweeteners: Allulose:
- Regulatory Recognition: GRAS status in the U.S. and novel food approval in the EU.
- Safety Attributes: Low caloric impact, minimal impact on blood sugar, with potential mild gastrointestinal effects at higher doses.
Stevia:
- Regulatory Recognition: GRAS status in the U.S., approved by EFSA in the EU.
- Safety Attributes: Zero-calorie nature, negligible impact on blood sugar, with potential mild aftertaste and considerations related to processing methods.
Navigating the Safety Horizon: A Closer Look
In the intricate tapestry of regulatory approvals and safety considerations, Allulose and Stevia emerge as players with validated credentials. The acknowledgment of their safety by regulatory bodies establishes a foundation of trust, assuring consumers of their suitability as sugar substitutes. As individuals navigate the sweet terrain of these alternatives, the comparative analysis sheds light on their safety attributes, emphasizing the importance of moderation for a harmonious integration into dietary choices. In the world of alternative sweeteners, the safety of Allulose and Stevia isn’t just a regulatory requirement; it’s a testament to their commitment to offering sweetness without compromise.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
In the dynamic landscape of dietary choices, consumer preferences wield considerable influence, steering the trajectory of market trends in the realm of alternative sweeteners, notably Allulose and Stevia. Understanding the nuances of these preferences and the broader market dynamics becomes pivotal in unraveling the factors that shape the choice between these two sweet alternatives in the vast spectrum of food products.
Understanding Consumer Preferences for Allulose and Stevia: Taste and Flavor Profile:
- Allulose, with its similarity to sucrose, resonates with consumers seeking a taste akin to traditional sugar without the associated caloric impact.
- Stevia appeals to those embracing a plant-based sweetener, appreciating its natural origin and distinct, albeit slightly different, flavor profile.
Health Conscious Choices:
- Consumers navigating health-conscious lifestyles may lean towards Allulose due to its low-calorie nature and minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
- Stevia’s zero-calorie attribute aligns with the preferences of those emphasizing weight management and sugar reduction in their diets.
Market Trends and the Growing Demand for Alternative Sweeteners: Shift Towards Healthier Options:
- The global market witnesses a significant shift towards healthier dietary choices, propelling the demand for alternative sweeteners like Allulose and Stevia.
- Increased awareness of the adverse effects of excessive sugar consumption fuels the surge in popularity for these sugar substitutes.
Innovation in Food and Beverage Industry:
- The food and beverage industry responds to consumer demand by incorporating Allulose and Stevia into a myriad of products, from beverages to baked goods.
- Innovations in product formulations cater to diverse preferences, expanding the availability of these sweeteners in the market.
Factors Influencing the Choice Between Allulose and Stevia in Food Products: Application Versatility:
- Allulose’s ability to mirror the taste and texture of sugar makes it versatile in various culinary applications, from baking to beverages.
- Stevia’s plant-based nature and unique flavor profile find favor in products where a distinctive taste is desired.
Labeling and Perception:
- Consumer perception of “natural” and “plant-based” influences the choice between Allulose and Stevia, with Stevia often associated with a more natural image.
- Labeling and marketing strategies play a role in shaping consumer preferences, as perceived health benefits become key decision-making factors.
Cost Considerations:
- The cost of production and market pricing contribute to the choice between Allulose and Stevia, with affordability impacting accessibility for a broader consumer base.
Navigating the Sweet Symphony: A Closer Look
As Allulose and Stevia take center stage in the sweetener landscape, consumer preferences and market trends harmonize to create a diverse and dynamic melody. The synergy between taste preferences, health-conscious choices, and innovative applications propels these sweet alternatives into mainstream culinary consciousness. Navigating the sweet symphony requires a nuanced understanding of the factors influencing consumer decisions, ensuring that the choices between Allulose and Stevia not only cater to individual tastes but also align with the evolving tapestry of health and wellness in the modern food landscape.
Expert Opinions and Studies
In the pursuit of sweetening options that align with both palatability and health considerations, the scientific community has delved into exhaustive studies examining the properties of Allulose and Stevia. Summarizing the findings from these scientific inquiries offers a comprehensive understanding of their impact on health.
Summarizing Findings from Scientific Studies on Allulose:
- Metabolic Impact: Scientific studies consistently highlight Allulose’s intriguing metabolic characteristics, showcasing its ability to provide sweetness without significantly impacting blood glucose levels.
- Caloric Profile: Researchers emphasize the low-calorie nature of Allulose, positioning it as a promising alternative for individuals aiming to reduce caloric intake without compromising taste.
Presenting Expert Opinions on Stevia and its Impact on Health:
- Natural Origin: Experts often underscore Stevia’s appeal as a natural sweetener derived from plant sources, aligning with the growing consumer preference for plant-based alternatives.
- Blood Sugar and Weight Management: Some studies and expert opinions point to Stevia’s potential benefits in blood sugar management and weight control, making it an attractive option for those with specific health goals.
A Balanced Assessment Based on Current Research:
- Comparative Analysis: A balanced assessment considers the contrasting attributes of Allulose and Stevia, acknowledging Allulose’s chemical similarity to sucrose and Stevia’s unique glycoside compounds.
- Taste Perception: Current research indicates that individual taste preferences play a crucial role in determining the suitability of Allulose and Stevia, with some consumers favoring one over the other based on perceived aftertastes or flavor nuances.
Navigating the Landscape: Insights from Experts and Studies
Navigating the landscape of sweeteners requires a nuanced understanding of expert opinions and the robust body of scientific studies shaping the discourse. As consumers seek alternatives that harmonize taste and health, the insights garnered from these studies serve as beacons, illuminating the paths towards informed choices. The synergy of scientific evidence and expert perspectives facilitates a nuanced exploration of Allulose and Stevia, ensuring that individuals can make choices aligned with their dietary preferences and health objectives. In the evolving narrative of sweeteners, expert opinions and rigorous research propel the discourse forward, providing clarity in the quest for sweetness without compromise.
Related questions and answers
- What are the differences between allulose and stevia?
Allulose and Stevia differ in origin, taste, and composition. Allulose, a monosaccharide, is chemically akin to fructose but with distinct metabolism, providing sweetness with minimal impact on blood sugar. It’s often derived from natural sources like fruits. Stevia, on the other hand, is a plant-based sweetener extracted from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant. While Allulose mimics the taste and texture of sugar, Stevia can have a slightly different flavor profile, with a hint of herbal notes. Importantly, Allulose contributes calories, albeit fewer than sugar, whereas Stevia is calorie-free. Both are popular alternatives, and the choice depends on taste preferences, dietary goals, and the desired sweetness experience.
- Are there any health concerns associated with using allulose?
While generally regarded as safe, using Allulose may prompt some digestive discomfort in high amounts, such as bloating or diarrhea, as the body may not fully absorb it. However, such effects vary among individuals. Importantly, Allulose doesn’t significantly impact blood sugar, making it a favorable choice for those monitoring glucose levels. Nevertheless, individuals with sensitivities or pre-existing digestive conditions should exercise moderation. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating Allulose into the diet, especially for those with specific health concerns or undergoing medical treatments. Overall, responsible consumption aligns with a balanced and informed approach, ensuring that the potential benefits of Allulose, such as reduced calorie intake, are balanced with individual health considerations.
- What is the regulatory status of stevia and allulose?
Both Stevia and Allulose have attained regulatory approval, affirming their safety for consumption. Stevia, approved by multiple regulatory agencies globally, including the FDA and EFSA, is recognized as a natural sweetener derived from the Stevia rebaudiana plant. It has widespread acceptance as a sugar substitute in various food and beverage products. Similarly, Allulose has gained regulatory approval in several countries, including the United States and Japan, with official recognition for its use as a low-calorie sweetener. As with any food ingredient, adherence to recommended consumption levels is advised. The regulatory green lights for both Stevia and Allulose underscore their compliance with safety standards, providing consumers with confidence in incorporating these sweeteners into their dietary choices.
- Do allulose and stevia have an impact on blood sugar levels?
Allulose and Stevia distinctly impact blood sugar levels. Allulose, despite its sweet taste, is not fully metabolized by the body, leading to minimal effects on blood glucose. It offers a diabetic-friendly alternative as it doesn’t cause significant spikes in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, Stevia, a natural sweetener derived from plant leaves, doesn’t affect blood sugar, making it a suitable choice for those monitoring glucose levels. Both sweeteners present viable options for individuals seeking sweetness without compromising on blood sugar management, aligning with the preferences of those with diabetes or those adopting low-glycemic diets.
- What are the potential health benefits of consuming stevia?
Consuming stevia can offer several potential health benefits. Firstly, it is a calorie-free alternative to sugar, aiding in weight management and calorie reduction. Stevia has also been associated with improved insulin sensitivity, making it a suitable option for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of insulin resistance. Additionally, stevia may contribute to better oral health, as it doesn’t cause tooth decay. Some studies suggest potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in stevia, offering support against oxidative stress. As a natural sweetener with a plant origin, stevia provides sweetness without the calories, making it a valuable choice for those seeking to maintain a healthy lifestyle while satisfying their sweet cravings.










